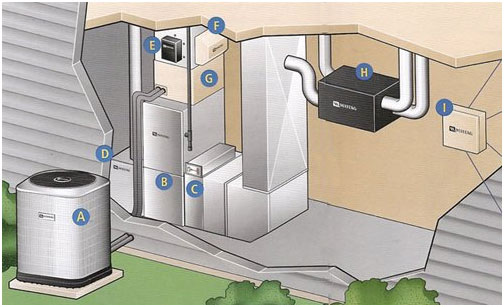
Learn How Your Air Conditioning Works
Your air conditioning system is comprised of many components that all have a role in cooling your dwelling.
Outside Condenser Coil or Heat Pump
This is a compressor inside the unit that provides compression for the system. This compression causes the cooling vapor to heat up. The compressed vapor is then cooled by heat exchange with the outside air so that the vapor condenses to a fluid.
The fluid is then pumped to the inside of the building, where it enters the evaporator coil. The fan mounted on the top of the unit forces the warm air created by the compressor out of the unit, which keeps the compressor from overheating. All new condensers must have at least a 14 SEER Efficiency Rating. (A on diagram)
Air Handler
The air handler is is used in the air conditioning process to blow or draw warm air over the evaporator coil. This cools the air and then blows the cool air into the existing ductwork. All new air handlers must have at least a 14 SEER Efficiency Rating. (B on diagram)
Electronic Air Cleaner
An electronic air cleaner is an electrically-charged filter installed between the existing ductwork and the furnace or air handler. This creates an electric charge which collects the particles on the built-in filters like a magnet. Electronic air cleaners are more energy efficient than HEPA Air Cleaners and eliminate the need to replace filters. In fact, certain brands can eliminate up to 99.98% of airborne particles and allergens. (C on diagram)
HEPA Air Cleaner
A HEPA air cleaner has some of the same benefits that an electronic air cleaner and they are very effective at removing airborne particles, although, filter replacement is periodically necessary. (C on diagram)
Ultra-Violet Air Purifier
An ultra-violet air purifier is usually used in conjunction with an electronic air cleaner or HEPA air cleaner. These purifiers are highly effective at eliminating airborne bacteria and viruses. (E on diagram)
Humidifier
A humidifier is used to maintain proper moisture levels in the home. (D on diagram)
Evaporator Coil
Inside the evaporator coil, small spray nozzles inject coolant into a chamber, where the pressure drops and the fluid evaporates. Since the evaporation absorbs heat, the surroundings cool off. The evaporator coil absorbs or adds heat to the system and the vapor is then returned to the compressor. A metering device acts as a restriction in the system to ensure that the heat being absorbed at the proper rate. (G on diagram)
Energy/Heat Recovery Ventilator (ERV/HRV)
HRVs and ERVs recover heat energy in exhaust air, then transfer it to fresh air as it enters the home. They ultimately provide fresh air and improved climate control while also saving energy by reducing the heating and cooling requirements. ERVs, unlike HRVs, also transfer the humidity of the exhaust air to the intake air. (F & H on diagram)
Zone Control Panel
The zone control panel allows your heating and cooling system to be set up in zones which are run by multiple programmable thermostats. Additionally, it also allows homeowners to have certain areas of the home warmer or cooler than other areas. (I on diagram)
Now that you have an idea of how the various components of your air conditioning works, make sure you invest in regular maintenance to keep it running reliably when you need it most! Call 3H AC today to schedule a maintenance appointment for your HVAC system.